Quick Summary:
- Sharps waste is classified as clinical and hazardous waste in the UK and requires careful handling and disposal to prevent health risks and environmental harm.
- The disposal journey includes proper collection in sharps bins, secure storage, licensed transportation, and treatment methods like autoclaving or incineration.
Proper management of sharps waste is a critical concern for businesses across various sectors, especially those dealing with medical or hazardous materials.
As a UK business owner, understanding the complete journey of sharps waste is essential for ensuring compliance with stringent regulations and safeguarding public health.
This guide provides an overview of what happens to sharps waste, highlighting key stages in its disposal process and offering best practices for effective waste management.
Table of Contents
- Waste Classification of Sharps
- The Disposal Journey of Sharps Waste
- Transportation of Sharps Waste
- Treatment Methods for Sharps Waste
- Final Disposal of Sharps Waste
- Ensuring Compliance and Best Practices
- Conclusion
Waste Classification of Sharps
What Waste Classification is Sharps?
Sharps are classified as hazardous waste in the UK. This classification stems from their potential to cause injuries and spread infections.
Specifically, sharps fall under the category of “special waste” as defined by the Hazardous Waste Regulations 2005. This means they require careful handling, segregation, and disposal to prevent harm to individuals and the environment.
Are Sharps a Biological Hazard?
Indeed, sharps can be a biological hazard.
Often coming into contact with bodily fluids, sharps have the potential to transmit infectious diseases such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HIV.
The biological risk associated with sharps necessitates stringent safety measures during handling and disposal to mitigate these health risks effectively.
The Disposal Journey of Sharps Waste

Collection and Segregation
Initially, sharps waste is collected in sharps waste bins specifically designed for this purpose. These bins are typically puncture-resistant and equipped with secure lids to prevent accidental exposure.
Proper segregation at the source is essential to ensure that sharps do not mix with other types of waste, which can complicate the disposal process and increase risk.
Storage Before Disposal
After collection, sharps waste is securely stored until it can be transported for treatment. Storage areas must be clearly marked and accessible only to trained personnel.
These areas are designed to minimise the risk of accidental injury and prevent unauthorised access, ensuring that sharps waste is safely contained.
Transportation of Sharps Waste
Licensing and Regulations
Transportation of sharps waste must comply with UK regulations to ensure safe and lawful movement. Licensed waste carriers are responsible for transporting sharps from the collection site to treatment facilities.
The transportation process involves strict adherence to safety protocols, including the use of specialised vehicles and the provision of appropriate documentation.
Documentation and Tracking
Throughout the transportation process, detailed documentation is required. This includes waste transfer notes and consignment notes that track the movement of sharps waste from the point of origin to the treatment facility.
Accurate record-keeping ensures regulatory compliance and provides an audit trail for accountability.
Treatment Methods for Sharps Waste
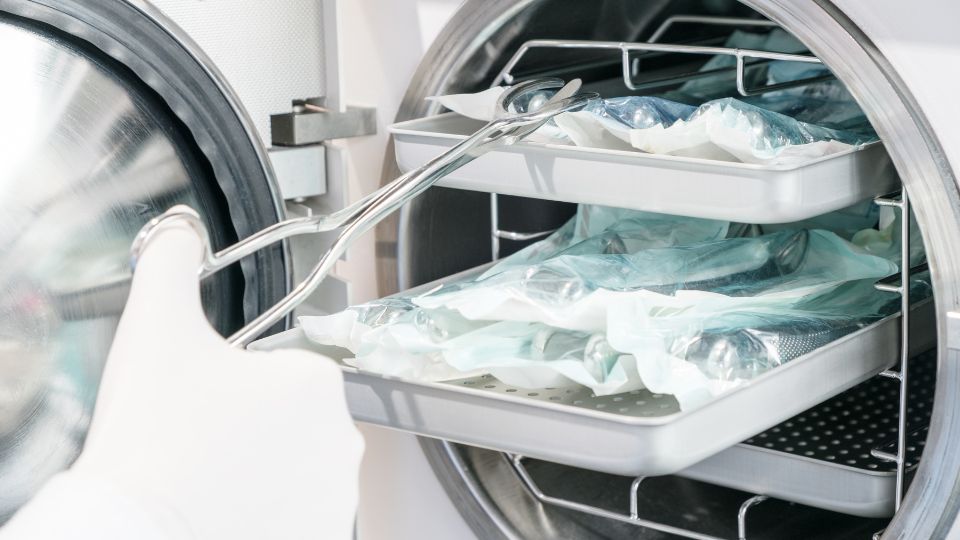

Autoclaving
One common method for treating sharps waste is autoclaving. This process uses high-pressure steam to sterilise the waste, rendering it safe for further handling.
Autoclaving effectively destroys pathogens and reduces the risk of infection. Once sterilised, the waste can be safely processed or disposed of in a non-hazardous manner.
Incineration
Another method for dealing with sharps waste is incineration. Incineration involves burning the waste at high temperatures, which destroys the hazardous components and reduces the volume of waste.
This method is particularly effective for eliminating biological and chemical contaminants, ensuring that no harmful substances are released into the environment.
Final Disposal of Sharps Waste
Landfill Disposal
After treatment, sharps waste may be disposed of in a landfill, but only if it has been treated to a non-hazardous state. It is crucial to ensure that any sharps waste sent to landfills meets the regulatory requirements for safe disposal. This typically involves treating the waste to neutralise its hazardous properties before landfilling.
Alternative Disposal Methods
In some cases, alternative disposal methods such as waste-to-energy may be used. These methods involve converting waste into energy through processes like incineration with energy recovery. This approach helps reduce the volume of waste and generates energy, contributing to sustainability efforts.
Ensuring Compliance and Best Practices

Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with UK regulations is mandatory for businesses managing sharps waste. This includes adhering to guidelines set out by the Environment Agency and the Hazardous Waste Regulations.
Regular audits and reviews of waste management practices can help ensure that your business remains compliant and avoids potential penalties
Conclusion
In summary, the journey of sharps waste involves careful collection, storage, transportation, treatment, and final disposal. Understanding and adhering to the regulatory requirements at each stage is essential for ensuring safety and compliance.
Business owners should take proactive steps to manage sharps waste responsibly by following best practices, maintaining compliance with regulations, and investing in effective waste management solutions.