In the wake of climate change, resource scarcity, and growing concerns about sustainability, the concept of the circular economy has gained significant traction.
Businesses across the UK are increasingly adopting circular economy principles to mitigate environmental impact, reduce waste, and drive long-term economic growth.
In this guide, we’ll be discussing what the term circular economy actually means, its principles, the benefits and its relevance to businesses and people living in the UK.
Table of Contents
- What Does Circular Economy Mean?
- Circular Economy Principles
- The Circular Economy and Climate Change
- Circular Economy Laws and Regulations in the UK
- Benefits of the Circular Economy
- Circular Economy Facts & Statistics:
- Conclusion

What Does Circular Economy Mean?
Simply put, the term Circular Economy is about using resources wisely by reusing, repairing, and recycling things instead of throwing them away so there is as close to zero waste as possible.
The circular economy is a systemic approach to economic development designed to benefit businesses, society, and the environment.
Unlike the traditional linear economy model of “take, make, dispose,” the circular economy aims to minimise waste and maximise the value of resources by keeping products and materials in use for as long as possible through strategies such as reuse, repair, remanufacturing, and recycling.

Circular Economy Principles
In today’s landscape where the economy is constantly changing, and consumers are developing a bigger need for sustainable products and practices, the methods of circular economy have never been more relevant.
As businesses grapple with the challenges posed by climate change, resource depletion, and waste generation, the circular economy emerges as a beacon of hope – a transformative framework that offers a path towards a more sustainable future.
At the heart of the circular economy lies a set of guiding principles aimed at reshaping traditional linear models of production and consumption.
In this section, we explore these principles in depth, explaining their significance and the transformative potential they hold for businesses across the UK.
1. Design for Longevity and Reusability
Businesses should prioritise designing products with longevity and reusability in mind, aiming to extend their lifecycle and reduce the need for frequent replacements.
This involves incorporating features such as modular design, the use of sustainable materials, and ensuring products are easily disassembled for repair or upgrade.
2. Resource Efficiency and Recycling within the Circular Economy
Maximising the value of resources is key in the circular economy.
This involves recycling materials, components, and products at the end of their lifecycle, as well as implementing closed-loop systems where materials are continuously reused or recycled.
3. Renewable Energy Integration
Transitioning to renewable energy sources is crucial for businesses looking to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions.
Integration of solar, wind, and other renewable energy technologies into business operations can significantly contribute to achieving sustainability goals.
4. Zero Waste Strategies
Implementing zero-waste strategies involves minimising waste generation at every stage of the product lifecycle.
This can be achieved through practices such as lean manufacturing, waste-to-energy conversion, composting, and adopting circular approaches to packaging and product design.

The Circular Economy and Climate Change
The circular economy is not only an innovative economic model but also a powerful tool in the fight against climate change.
By fundamentally re-imagining the way goods are produced, consumed, and disposed of, the circular economy offers a holistic approach to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving resources, and promoting sustainable practices.
One of the most significant contributions of the circular economy to climate change mitigation lies in its ability to minimise waste and extend the lifespan of products and materials.
In a traditional linear economy, products are often designed for single-use or short-term consumption, leading to rapid resource depletion and increased emissions associated with extraction, production, and disposal.
However, in a circular economy, products are designed with durability and reusability in mind, thereby reducing the need for frequent replacements and the associated emissions.
Additionally, the emphasis on resource efficiency and recycling in the circular economy helps to conserve finite resources and reduce the environmental footprint of production processes.
By maximising the value extracted from materials and keeping them in circulation for as long as possible, the circular economy reduces the demand for virgin resources, which often require energy-intensive extraction methods and contribute to deforestation, habitat destruction, and biodiversity loss.
Research conducted by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation highlights the significant potential of transitioning to a circular economy in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Did You Know: a shift towards circularity could cut global greenhouse gas emissions by an impressive 39% by the year 2050?
This reduction stems from various factors, including the decreased reliance on energy-intensive extraction and production processes, the avoidance of emissions associated with landfilling and incineration, and the overall optimisation of resource use throughout the product lifecycle.
In essence, the circular economy offers a multifaceted approach to addressing the interconnected challenges of climate change and unsustainable resource consumption.
By adopting circular principles and practices, businesses and governments can not only reduce their environmental impact but also unlock new opportunities for innovation, economic growth, and long-term resilience in the face of global environmental challenges.

Circular Economy Laws and Regulations in the UK
The UK government has demonstrated a strong commitment to advancing the circular economy through legislation and regulatory measures in recent years.
These initiatives aim to increase sustainability, reduce waste, and promote resource efficiency across various business sectors.
Here are some key regulations and programmes:
Waste and Resources Action Programme (WRAP)
The Waste and Resources Action Programme (WRAP) is a prominent organisation you may have already heard of.
They collaborate with businesses, governments, and communities to promote resource efficiency and waste reduction.
WRAP provides guidance, support, and funding to help businesses implement sustainable practices and reduce their environmental impact.
Environment Act 2021
The Environment Act 2021 represents a significant legislative effort to address environmental challenges and promote the circular economy in the UK.
This legislation includes provisions for extended producer responsibility schemes, which hold manufacturers accountable for the environmental impact of their products throughout their lifecycle.
Additionally, the bill introduces deposit-return systems to encourage recycling and measures to tackle plastic pollution, such as restrictions on single-use plastics and initiatives to promote plastic recycling.
UK Plastics Pact
The UK Plastics Pact is a collaborative initiative led by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, bringing together businesses, non-governmental organisations (NGOs), and government agencies to eliminate unnecessary single-use plastics and promote recycling.
Members of the pact commit to ambitious targets for reducing plastic waste and increasing the recyclability of plastic packaging.
Through collective action and innovation, the UK Plastics Pact aims to create a circular economy for plastics, where materials are used, collected, and recycled effectively to minimise environmental impact.
These laws and regulations represent significant steps towards building a more sustainable and circular economy in the UK.
By implementing these measures, businesses and policymakers can work together to reduce waste, conserve resources, and create a more resilient and environmentally friendly society.
Landfill Tax
The UK government imposes a Landfill Tax to discourage the disposal of waste in landfills.
This tax incentivises businesses to adopt waste management practices that prioritise recycling, reuse, and waste reduction.
Producer Responsibility Obligations (Packaging Waste) Regulations
The Producer Responsibility Obligations place restrictions and responsibility on businesses that produce or handle packaging materials.
Producers are required to finance the recovery and recycling of packaging waste, encouraging the use of recyclable materials and reducing packaging waste.
Energy Savings Opportunity Scheme (ESOS)
ESOS is a mandatory energy assessment and energy-saving identification scheme for large UK businesses.
Compliance with ESOS involves identifying energy-saving opportunities, which may include improvements in resource efficiency and waste reduction.
Plastic Packaging Tax
Scheduled to be implemented in April 2022, the Plastic Packaging Tax aims to reduce the use of plastic packaging containing less than 30% recycled content.
This tax will incentivise the use of recycled materials in packaging and encourage the adoption of more sustainable packaging solutions.

Benefits of the Circular Economy
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, the circular economy has emerged as a compelling framework for driving sustainability and innovation.
By transitioning from a linear “take-make-dispose” model to one that prioritises resource efficiency, waste reduction, and reuse, businesses can unlock a lot of benefits for both the environment and their bottom line.
In this section, we explore the multiple advantages of embracing the circular economy, from reducing environmental impact and conserving resources to encouraging financial resilience and driving economic growth.
Environmental Benefits:
- Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
- Conservation of natural resources and biodiversity.
- Minimisation of waste sent to landfills and oceans.
Economic Benefits:
- Cost savings through resource efficiency and waste reduction.
- Job creation in industries such as recycling, remanufacturing, and renewable energy.
- Enhanced resilience to supply chain disruptions.
Social Benefits:
- Improved public health through reduced pollution and waste.
- Enhanced community engagement and empowerment.
- Access to affordable, sustainable products and services for all.

Circular Economy Facts & Statistics:
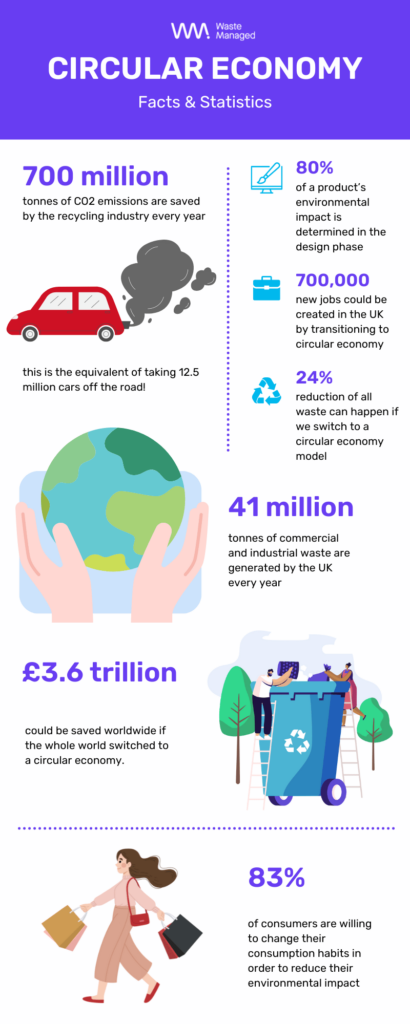
- Over 80% of a product’s environmental impact is determined during the design phase.
- The UK generates around 41 million tonnes of commercial and industrial waste annually, highlighting the urgency for circular economy practices.
- Circular economy initiatives could generate £75 billion in economic benefits for the UK by 2030.
- Transitioning to a circular economy could generate £3.6 trillion for the globe.
- The circular economy has the potential to create 700,000 new jobs across the UK.
- A study by the European Commission found that implementing circular economy principles could reduce total waste generation in the EU by 24% by 2030.
- The UK recycling industry saves more than 700 million tonnes of CO2 emissions annually, equivalent to taking 12.5 million cars off the road each year!
- A survey conducted by Accenture found that 83% of consumers are willing to change their consumption habits to reduce environmental impact, indicating growing demand for circular economy products and services.
Conclusion
The circular economy represents a paradigm shift in how businesses operate, emphasising sustainability, resource efficiency, and innovation.
By embracing circular economy principles, UK businesses can not only reduce their environmental footprint but also drive economic growth and create a more resilient, equitable society.
As the world moves towards a net-zero future, the circular economy offers a viable pathway towards a more sustainable and prosperous future for all.








