Quick Summary:
- Ensure biohazard waste is correctly identified, segregated, and disposed of using appropriate methods such as autoclaving, incineration, or chemical treatment.
- Follow local regulations for biohazard waste disposal and maintain thorough documentation and training to ensure safety and legal compliance.
Biohazard waste disposal is a absolutely crucial to do correctly.
Disposing of biohazard waste appropriately is crucial for safeguarding public health, protecting the environment, and ensuring legal compliance.
Whether you’re dealing with clinical waste from a healthcare facility, laboratory waste, or other biohazardous materials you must understand the proper procedures.
Here’s a detailed guide to help you navigate the complexities of biohazard waste disposal.
Table of Contents
Understanding Biohazard Waste

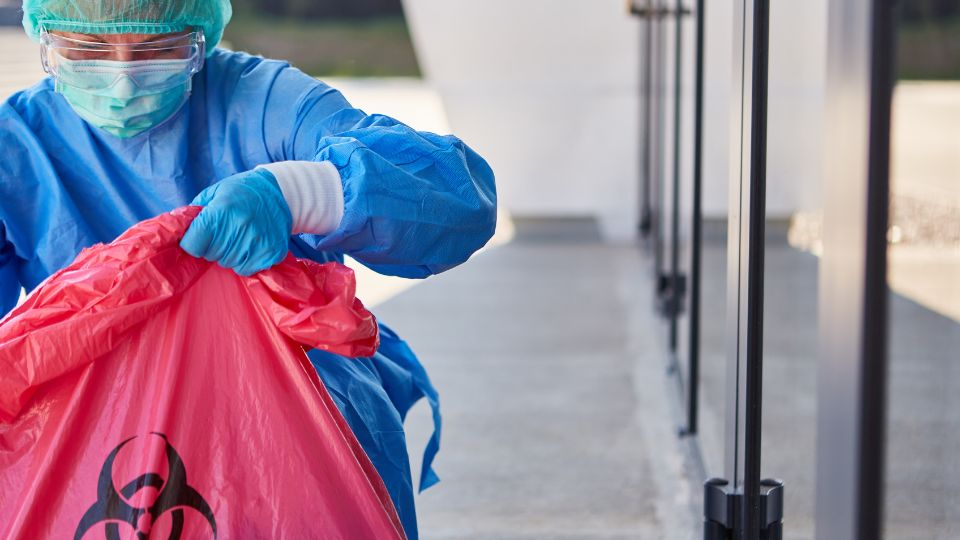
Biohazard waste refers to materials that risk human health or the environment due to their biological nature.
This includes, but is not limited to:
- Medical Waste – Items such as used syringes, blood-soaked bandages, and other materials from healthcare settings.
- Clinical Waste – A subset of medical waste, including waste from hospitals and clinics contaminated with pathogens or other biological hazards.
- Laboratory Waste – Contaminated materials from research or diagnostic labs.
- Pathological Waste – Human or animal tissues and body parts.
- Pharmaceutical Waste – Expired or unused medications.
- Hazardous Waste – Includes both chemical and biological hazards that require specific disposal methods.
- Sharps – Items that can puncture or cut, such as needles, blades, and broken glass.
Steps for Proper Disposal

1. Identify and Segregate Waste
Properly identifying and segregating biohazard waste is essential to ensure each type of waste is treated and disposed of according to its specific requirements.
- Medical Waste – Use puncture-resistant, leak-proof containers. Label them with biohazard symbols.
- Clinical Waste – Similar to medical waste, but may require more stringent handling and disposal procedures due to a higher risk of infection.
- Hazardous Waste – Includes both chemical and biological components. Follow specific guidelines for each type.
- Sharps – Store in specially designed sharps containers that are puncture-proof and leak-proof.
2. Follow Local Regulations
In the UK, follow regulations set by the Environment Agency and follow the guidelines provided by the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) for biohazard waste disposal.
3. Choose Appropriate Disposal Methods

The method of disposal depends on the type and quantity of waste.
Common methods include:
- Autoclaving – Sterilises waste by steam under pressure. Commonly used for medical and clinical waste.
- Incineration – Burns waste at high temperatures. Suitable for sharps, pathological waste, and some hazardous materials.
- Chemical Treatment – Neutralises hazardous substances. Often used for certain types of pharmaceutical or chemical waste.
4. Engage Professional Services
For large quantities or complex types of biohazard waste, working with a licensed waste disposal company is advisable.
These professionals are trained to handle, transport, and dispose of biohazard waste safely and in compliance with regulations.
5. Training and Safety
Ensure that all personnel involved in handling biohazard waste are properly trained in safety procedures and waste management protocols.
This includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and understanding emergency procedures.
6. Documentation and Record Keeping
Maintain detailed records of waste generation, handling, and disposal. This documentation is often required for regulatory compliance and can also be useful in case of audits or inspections.
7. Public Awareness and Education
Promote awareness and education about the importance of proper biohazard waste disposal within your organisation or community. Proper knowledge helps prevent mishandling and promotes a culture of safety.
Conclusion
Proper disposal of biohazard waste, including clinical, medical, hazardous, and sharps waste, is not just a regulatory requirement but a critical aspect of environmental stewardship and public health.
By following the steps outlined above, you can ensure that biohazard waste is managed safely and effectively, minimising risks and contributing to a healthier and safer environment.
For more detailed information, always consult local regulations and industry best practices to ensure compliance and safety.